
The experimental variogram is found by calculating the variance (g) of each point in the set with respect to each of the other points and plotting the variances versus distance (h) between the points. Suppose that the value to be interpolated is referred to as f. A variogram consists of two parts: an experimental variogram and a model variogram. The first step in ordinary kriging is to construct a variogram from the scatter point set to be interpolated. There are several differences between 2D and 3D Kriging. The selection of the Kriging method and the definition of the variograms are accomplished using the Kriging Options dialog. Academic Press, New York, NY, 1978.Ī powerful set of kriging techniques with varying degrees of sophistication have been implemented in GMS.
EZ KRIGING SOFTWARE SOFTWARE
GSLIB: Geostatistical Software Library and User's Guide. It is strongly encouraged to refer the GSLIB textbook for more information:

Since kriging is a rather complex interpolation technique and includes numerous options, a complete description of kriging is beyond the scope of this reference manual. The kriging routines implemented in GMS are based on the Geostatistical Software Library (GSLIB) routines published by Deutsch and Journel (1992).
Kriging is a set of linear regression routines which minimize estimation variance from a predefined covariance model. A regionalized variable is intermediate between a truly random variable and a completely deterministic variable in that it varies in a continuous manner from one location to the next and therefore points that are near each other have a certain degree of spatial correlation, but points that are widely separated are statistically independent (Davis, 1986). Kriging is based on the assumption that the parameter being interpolated can be treated as a regionalized variable. Over the past several decades kriging has become a fundamental tool in the field of geostatistics.
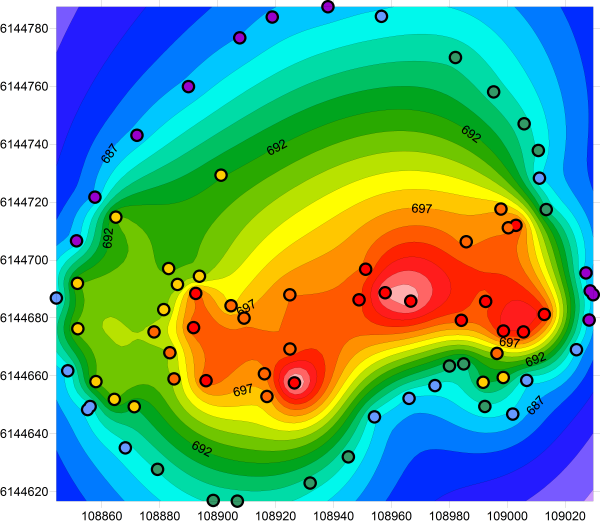
Krige who developed the technique in an attempt to more accurately predict ore reserves. Kriging is a method of interpolation named after a South African mining engineer named D.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
